

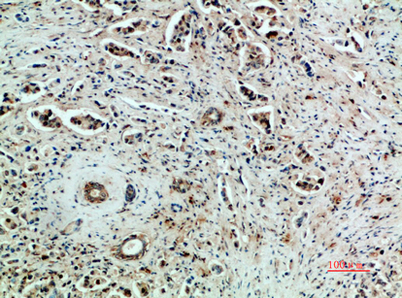
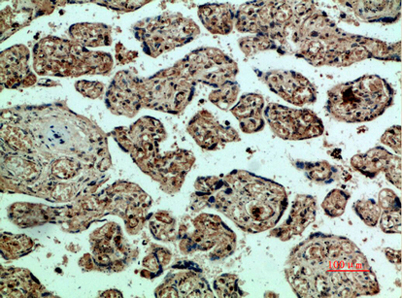



Flk-1/VEGFR2 rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | Flk-1/VEGFR2 rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human; |
| Alternative Names: | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2;EC 2.7.10.1;Fetal liver kinase 1;FLK-1;Kinase insert domain receptor;KDR;Protein-tyrosine kinase receptor flk-1;CD antigen CD309) |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | IF: 1:50-200 Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. IHC-p: 1:100-300 ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | Synthetic peptide from human protein at AA range: 1268-1341 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| GeneID: | 3791 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | P35968 |
| Cellular localization: | Cell junction . Endoplasmic reticulum . Cell membrane . Localized with RAP1A at cell-cell junctions (By similarity). Colocalizes with ERN1 and XBP1 in the endoplasmic reticulum in endothelial cells in a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent manner (PubMed:23529610). .; [Isoform 1]: Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasmic vesicle. Early endosome. Detected on caveolae-enriched lipid rafts at the cell surface. Is recycled from the plasma membrane to endosomes and back again. Phosphorylation triggered by VEGFA binding promotes internalization and subsequent degradation. VEGFA binding triggers internalization and translocation to the nucleus.; [Isoform 2]: Secreted .; [Isoform 3]: Secreted. |
| Background: | Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a major growth factor for endothelial cells. This gene encodes one of the two receptors of the VEGF. This receptor, known as kinase insert domain receptor, is a type III receptor tyrosine kinase. It functions as the main mediator of VEGF-induced endothelial proliferation, survival, migration, tubular morphogenesis and sprouting. The signalling and trafficking of this receptor are regulated by multiple factors, including Rab GTPase, P2Y purine nucleotide receptor, integrin alphaVbeta3, T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase, etc.. Mutations of this gene are implicated in infantile capillary hemangiomas. [provided by RefSeq, May 2009], |

 Manual
Manual