







α-SMA rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | α-SMA rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | ACTA1; ACTA; Actin, alpha skeletal muscle; Alpha-actin-1; ACTA2; ACTSA; ACTVS; GIG46; Actin, aortic smooth muscle; Alpha-actin-2; Cell growth-inhibiting gene 46 protein; ACTC1; ACTC; Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1; Alpha-cardiac actinACTA1; ACTA; Actin, alpha skeletal muscle; Alpha-actin-1; ACTA2; ACTSA; ACTVS; GIG46; Actin, aortic smooth muscle; Alpha-actin-2; Cell growth-inhibiting gene 46 protein; ACTC1; ACTC; Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1; Alpha-cardiac actin |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. IHC-p: 1:100-300 ELISA: 1/20000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | Synthesized peptide derived from the C-terminal region of human α-SMA. |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 42kD |
| GeneID: | 59 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | P68133 |
| Cellular localization: | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. |
| Background: | The product encoded by this gene belongs to the actin family of proteins, which are highly conserved proteins that play a role in cell motility, structure and integrity. Alpha, beta and gamma actin isoforms have been identified, with alpha actins being a major constituent of the contractile apparatus, while beta and gamma actins are involved in the regulation of cell motility. This actin is an alpha actin that is found in skeletal muscle. Mutations in this gene cause nemaline myopathy type 3, congenital myopathy with excess of thin myofilaments, congenital myopathy with cores, and congenital myopathy with fiber-type disproportion, diseases that lead to muscle fiber defects. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008], |
-
 Western Blot analysis of MFC cells using α-SMA Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000
Western Blot analysis of MFC cells using α-SMA Polyclonal Antibody. Secondary antibody(catalog#:RS0002) was diluted at 1:20000 -
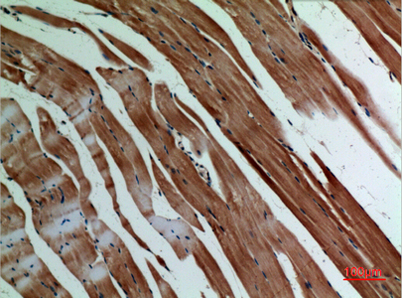
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100 -
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100 -
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse-muscle, antibody was diluted at 1:100

 Manual
Manual