





GAK rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | GAK rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse |
| Alternative Names: | GAK; Cyclin-G-associated kinase |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. Immunofluorescence: 1/200 - 1/1000. ELISA: 1/5000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human GAK. AA range:101-150 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 144kD |
| GeneID: | 2580 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | O14976 |
| Cellular localization: | Cytoplasm, perinuclear region . Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network . Cell junction, focal adhesion . Localizes to the perinuclear area and to the trans-Golgi network. Also seen on the plasma membrane, probably at focal adhesions. |
| Background: | cyclin G associated kinase(GAK) Homo sapiens In all eukaryotes, the cell cycle is governed by cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), whose activities are regulated by cyclins and CDK inhibitors in a diverse array of mechanisms that involve the control of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of Ser, Thr or Tyr residues. Cyclins are molecules that possess a consensus domain called the 'cyclin box.' In mammalian cells, 9 cyclin species have been identified, and they are referred to as cyclins A through I. Cyclin G is a direct transcriptional target of the p53 tumor suppressor gene product and thus functions downstream of p53. GAK is an association partner of cyclin G and CDK5. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2015], |
-
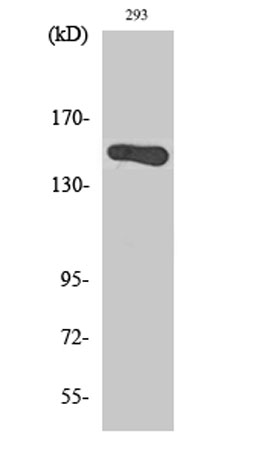
 Western Blot analysis of various cells using GAK Polyclonal Antibody
Western Blot analysis of various cells using GAK Polyclonal Antibody -
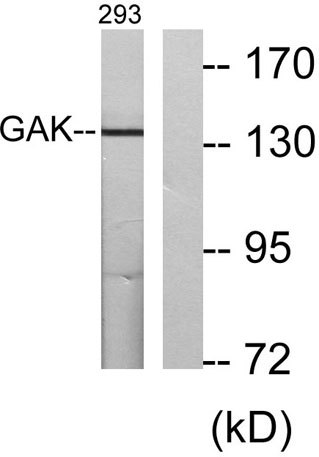
 Western blot analysis of lysates from 293 cells, using GAK Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from 293 cells, using GAK Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the synthesized peptide. -
 Western blot analysis of the lysates from HepG2 cells using GAK antibody.
Western blot analysis of the lysates from HepG2 cells using GAK antibody. -
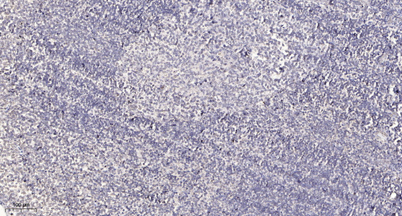
 Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 30min).
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil. 1, Antibody was diluted at 1:200(4° overnight). 2, Tris-EDTA,pH9.0 was used for antigen retrieval. 3,Secondary antibody was diluted at 1:200(room temperature, 30min).

 Manual
Manual