





Fnk rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | Fnk rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | PLK3; CNK; FNK; PRK; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK3; Cytokine-inducible serine/threonine-protein kinase; FGF-inducible kinase; Polo-like kinase 3; PLK-3; Proliferation-related kinase |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. ELISA: 1/10000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human PLK3. AA range:231-280 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
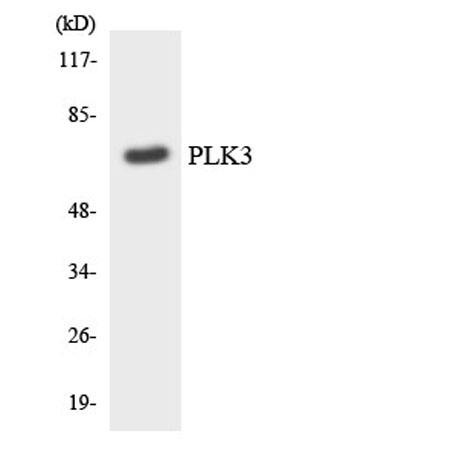
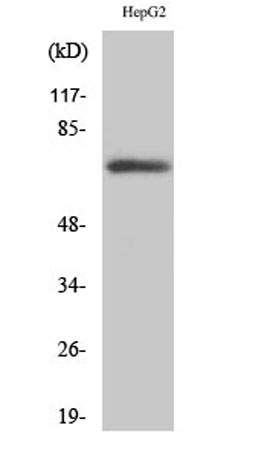
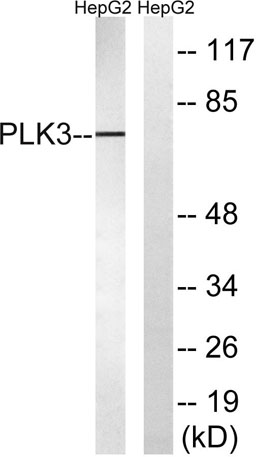
| Observed Band: | 70kD |
| GeneID: | 1263 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | Q9H4B4 |
| Cellular localization: | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus, nucleolus. Golgi apparatus. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Translocates to the nucleus upon cisplatin treatment. Localizes to the Golgi apparatus during interphase. According to a report, PLK3 localizes only in the nucleolus and not in the centrosome, or in any other location in the cytoplasm (PubMed:17264206). The discrepancies in results may be explained by the PLK3 antibody specificity, by cell line-specific expression or post-translational modifications. . |
| Background: | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the highly conserved polo-like kinase family of serine/threonine kinases. Members of this family are characterized by an amino-terminal kinase domain and a carboxy-terminal bipartite polo box domain that functions as a substrate-binding motif and a cellular localization signal. Polo-like kinases are important regulators of cell cycle progression. This gene has also been implicated in stress responses and double-strand break repair. In human cell lines, this protein is reported to associate with centrosomes in a microtubule-dependent manner, and during mitosis, the protein becomes localized to the mitotic apparatus. Expression of a kinase-defective mutant results in abnormal cell morphology caused by changes in microtubule dynamics and mitotic arrest followed by apoptosis. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015], |

 Manual
Manual