




GR (phospho Ser211) rabbit pAb
 One-click to copy product information
One-click to copy product information$148.00/50µL $248.00/100µL
| 50 µL | $148.00 |
| 100 µL | $248.00 |
Overview
| Product name: | GR (phospho Ser211) rabbit pAb |
| Reactivity: | Human;Mouse;Rat |
| Alternative Names: | NR3C1; GRL; Glucocorticoid receptor; GR; Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 1 |
| Source: | Rabbit |
| Dilutions: | Western Blot: 1/500 - 1/2000. Immunohistochemistry: 1/100 - 1/300. ELISA: 1/5000. Not yet tested in other applications. |
| Immunogen: | The antiserum was produced against synthesized peptide derived from human GR around the phosphorylation site of Ser211. AA range:181-230 |
| Storage: | -20°C/1 year |
| Clonality: | Polyclonal |
| Isotype: | IgG |
| Concentration: | 1 mg/ml |
| Observed Band: | 95kD |
| GeneID: | 2908 |
| Human Swiss-Prot No: | P04150 |
| Cellular localization: | [Isoform Alpha]: Cytoplasm . Nucleus . Mitochondrion . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle . Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome . After ligand activation, translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. In the presence of NR1D1 shows a time-dependent subcellular localization, localizing to the cytoplasm at ZT8 and to the nucleus at ZT20 (By similarity). Lacks this diurnal pattern of localization in the absence of NR1D1, localizing to both nucleus and the cytoplasm at ZT8 and ZT20 (By similarity). .; [Isoform Beta]: Nucleus . Cytoplasm . Expressed predominantly in the nucleus with some expression also detected in the cytoplasm. .; [Isoform Alpha-B]: Nucleus . Cytoplasm . After ligand activation, translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. . |
| Background: | This gene encodes glucocorticoid receptor, which can function both as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements in the promoters of glucocorticoid responsive genes to activate their transcription, and as a regulator of other transcription factors. This receptor is typically found in the cytoplasm, but upon ligand binding, is transported into the nucleus. It is involved in inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation, and differentiation in target tissues. Mutations in this gene are associated with generalized glucocorticoid resistance. Alternative splicing of this gene results in transcript variants encoding either the same or different isoforms. Additional isoforms resulting from the use of alternate in-frame translation initiation sites have also been described, and shown to be functional, displaying diverse cytoplasm-to-nucleus trafficking pat |
-
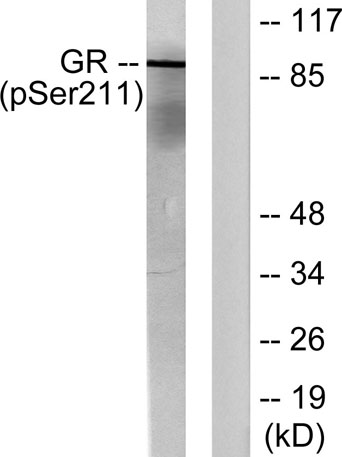
 Western Blot analysis of various cells using Phospho-GR (S211) Polyclonal Antibody
Western Blot analysis of various cells using Phospho-GR (S211) Polyclonal Antibody -
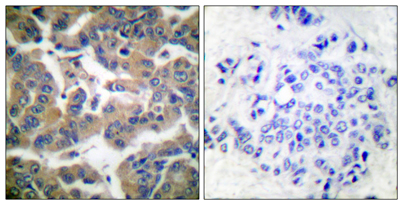
 Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma, using GR (Phospho-Ser211) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
Immunohistochemistry analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma, using GR (Phospho-Ser211) Antibody. The picture on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide. -
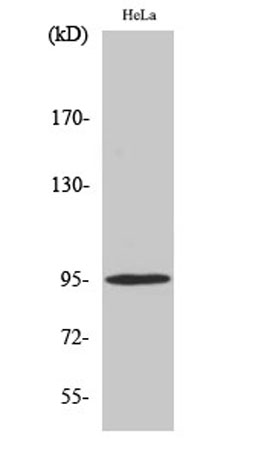
 Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa cells treated with Heat shock, using GR (Phospho-Ser211) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.
Western blot analysis of lysates from HeLa cells treated with Heat shock, using GR (Phospho-Ser211) Antibody. The lane on the right is blocked with the phospho peptide.

 Manual
Manual